SOCIALENERGY is a holistic S/W infrastructure to be used by today’s progressive electric utilities (or else Energy Service Providers - ESPs) towards the realization of their first steps in the digitization era of retail electricity markets.
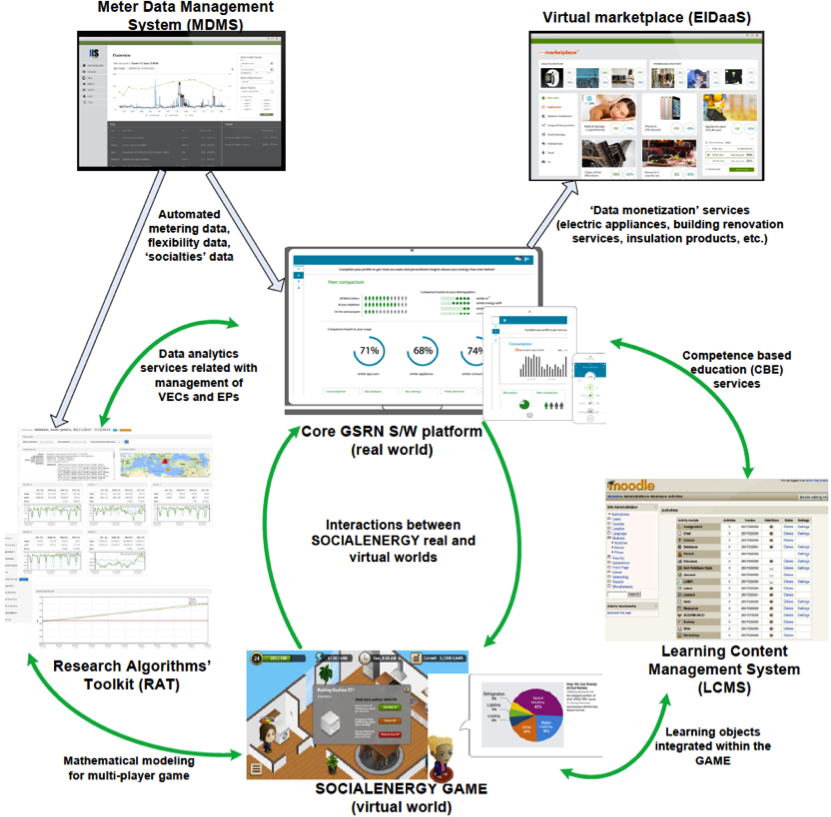
As illustrated in the figure above, SOCIALENERGY system comprises of six S/W components (subsystems), namely: 1) Meter Data Management System (MDMS), 2) the core GSRN S/W platform or else SOCIALENERGY’s real world, 3)Energy Efficiency GAME or else SOCIALENERGY’s virtual world, 4) Research Algorithms’ Toolkit (RAT), 5) Learning Content Management System (LCMS), and 6) Virtual marketplace.
Meter Data Management System (MDMS)
MDMS is the SOCIALENERGY’s database, where all energy metering data from all ESP’s customers is collected together with all energy-related data models (e.g., electric appliance consumption models, disaggregation data, home energy labelling models, etc.).
All types of SOCIALENERGY users (e.g. individual consumers, VEC leaders/managers, electric utility/retailer user, ESCO user, etc.) are able to log in the system via the core GSRN S/W platform interface. A single sign-in procedure takes place and then the user is able to navigate in all SOCIALENERGY subsystems. Indicatively, through GSRΝ, an individual consumer can select an Energy Program (EP) or participate in a Virtual Energy Community (VEC) in order to select a community EP that fits its needs. A utility user (e.g. utility’s CEO) is able to visualize the data of its entire customers portfolio and perform advanced administrative tasks, such as create new EPs, update reporting/recommendation rules of EP to its users, handle various business analytics, etc. A VEC leader can only have access to its associated VEC members’ profiles and perform respective tasks.
GSRN platform consists of several S/W modules. ‘Data Analytics’ module visualizes all RAT-API outputs and provides a visualized KPIs’ dashboard to the users in order to allow them to check their overall performance. ‘Energy module’ is connected to the MDMS-API and RAT-API in order to visualize real energy consumption curves (ECCs) from users’ meters and billing information respectively. ‘Gaming profile’ module connects directly to the GAME-API and gets all relevant details from the game, regarding each specific user. User gets badges, leader board, performance, stages, points and all available GAME-API inputs. Finally, ‘Socialties’ module is also working at the backend and is used to get user’s social network information, as the user logs in the system. It is also combined with all other modules to provide personalization and further analytics. ‘E-learning/training’ module is responsible for the integration and visualization of all educational material and relevant interactions coming from the GSRN-LCMS API. The rewarding mechanism works at the backend and computes the individual points for all users’ activity in the GSRN. It also connects to the GAME-API in order to feed the ‘User Profiling’ module with game leader-board and relevant points from the user’s game performance. The mechanism is flexible for the administrator to design the point system based on users’ stage, points and performance. Point system consists of two categories: ‘Actual points’ and ‘Experience points’, indicating activity and knowledge engagement correspondingly.
After the SOCIALENERGY user (i.e. individual consumer) is logged in the GSRN, s/he uses the same credentials to start the game. The SOCIALENERGY GAME can be played by the user in a range of platforms, starting from a basic web-based implementation and possibly be extended to a mobile application, too. The GAME is an applied game on energy efficiency and combines characteristics from serious games and the classic entertainment industry. The player creates/enters a virtual world (i.e., virtual house) with all electric appliances and tries to maximize the energy efficiency KPIs by striking to find an optimal trade-off between the energy cost (according to the EP that s/he selected) and the discomfort incurred through load shedding and shifting actions. Via the gameplay, the user is seamlessly educated in best practices about energy efficiency and this is done in an enjoying manner. Furthermore, the users can customize the GAME’s settings and customize the virtual environment that is more appealing to them. As a result, GAME can also serve as a (near) real-life testbed to help in quantifying user’s behavioural change through time, which is very important from both a research and commercial exploitation point of view. It should be noted that the GAME is also interacting with the RAT (by integrating all sophisticated mathematical modeling that modern EPs dispose, which provides the basis for the GAME’s long-term success in the market). GAME also incorporates references to educational material (e.g. in the form of small pop-up windows) that the users can find in the LCMS and search for more details therein. Finally, the multi-player feature of the GAME, through the use of virtual users (bots), allows the users to be educated on the operation of community EPs and the additional benefits that the latter can provide to the users.
Research Algorithms’ Toolkit (RAT)
From the GSRN S/W platform’s web interface, the utility user (i.e. system administrator) is able to select the “RAT” tab and then a new window navigates him/her to the RAT’s functionalities. The RAT subsystem is very important for SOCIALENERGY’s operation because it provides all the intelligence that is required towards making SOCIALENERGY S/W platform competitive enough and commercially successful in a sustainable manner. It provides all the EPs’ modeling and “data analytics” services mainly to GSRN and to the GAME (by integrating the sophisticated mathematical modeling in the energy pricing and game score calculations). Various research algorithms are executed regarding: i) the dynamic pricing models that are adopted in the various innovative EPs and ii) the VECs’ creation and dynamic adaptation algorithms (required for the online management of VECs). RAT is also a planning tool for the system administrator to automatically analyze various business/strategy ‘what-if’ scenarios by running parameterized system-level simulations.
Learning Content Management System (LCMS)
LCMS is the subsystem, where the user/player educates herself both online (e.g. via the gameplay or by taking various learning courses) and offline (e.g. by consuming CBE-based material) to consolidate the new knowledge about good practices on energy efficiency. LCMS interacts with GSRN. Thus, the latter can provide recommendation services to the user according to the educational content that is mostly keen on watching next based on user’s current educational profile and actions in SOCIALENERGY’s real and virtual worlds. The role of the LCMS is important, because it provides to the user the opportunity to better comprehend the new concepts in the liberalized smart grid markets and inter-relate the “lessons learned” from the GAME with the real-life conditions. In this way, end users are able to efficiently interact with their electric utility company. LCMS adopts a competence-based educational framework for energy efficiency. There are four main categories of competences: a) Energy-related end-user’s knowledge on various theoretical aspects of smart grids, dynamic pricing, energy efficiency, etc. b) Personal willingness to act based on each user’s activities inside the SOCIALENERGY platform, c) Social interactions behaviour based on the user’s activity inside the VEC, and d) Energy-related end-user’s skills based on the user’s achievements (e.g. % of energy savings, % bill reduction, etc.).
Finally, via the ‘virtual marketplace’ component, SOCIALENERGY bridges the gap between energy consumers and multiple other market stakeholders related to the energy efficiency sector. Via the use of SOCIALENERGY platform, the profile of each energy consumer is created (e.g. energy consumption history, social networking activities, commercial actions’ history, etc.). This profiling information can be exploited from stakeholders in order to: i) design energy efficiency products and services (e.g. offers for building renovation, insulation materials, etc.) more appealing to their audience, ii) allow VECs to contribute in the design of new or enhanced products/services by giving their opinions, iii) exploit VECs as cells within which group trading can be facilitated, and iv) generally sell Energy Information Distribution as a Service (EIDaaS) to whom it may concern in the long-term future. SOCIALENERGY has created an API through which it can commercialize this idea of “data monetization” service. Moreover, the virtual marketplace can host products and services from electric appliance vendors/retailers, building renovation companies, etc., so that the user can have an end-to-end experience on the way to achieve his/her energy efficiency targets. Ultimately, this business model can be very beneficial for the electric utility, too.


